About Maldives
Geography of Maldives
- Maldives, a Toll Gate in the Indian Ocean: Located at the southern and northern parts of this island chain lies the two important sea lanes of communication (SLOCs).
- These SLOCs are critical for maritime trade flow between the Gulf of Aden and Gulf of Hormuz in West Asia and the Strait of Malacca in Southeast Asia.
- Physical geography primarily consists of Coral Reefs and Atolls and most of the area is under Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs)
- Maldives primarily consists of an archipelago of low lying islands, which has been threatened due to rising sea rise.
- Eight Degree Channel separates Indian Minicoy (part of Lakshadweep Islands) from that of Maldives.
Political System of Maldives
- Maldives’ electoral system is similar to France, where the winner has to secure more than 50% of votes. If no one crosses the mark in the first round, in the second round, the top two candidates go head to head.
- Historically, Maldives had an Executive Presidency system since 1968, transitioning to a multi-party democracy in 2008. No incumbent president has been re-elected since then, which is concerning for India this time.
What is the Historical Background of India-Maldives Relations?
India and Maldives share ethnic, linguistic, cultural, religious, and commercial connections that date back to ancient times. The name Maldives is believed to be of Sanskrit origin (Mala (garland) + Dweep (Island)). The islands are believed to have been inhabited as early as 5th century BC by settlers from Sri Lanka and Southern India. There were close trade relationships between India and Maldives during ancient and medieval times.
Historical Evolution of India-Maldives Relations
| 1965 | In 1965, Maldives gained Independence from the British. India was one of the first countries to establish diplomatic relations with Maldives. Indian Mission was set up in Male in 1972. |
| 1978 | In 1978, President Maumoon Abdul Gayoom took charge in Maldives. Gayoom made many visits to India which strengthened India-Maldives ties. |
| 1988 | In 1988, India sent its troops and ships to help Gayoom overthrow a coup attempt by a Maldives businessman and Sri Lankan Tamil fighters. |
| 2008 | In 2008, Mohamed Nasheed was elected President. During his tenure, India began closer security cooperation with Maldives. India loaned 2 helicopters, dornier aircraft and patrol boats to Maldives. These were for maritime reconnaissance, surveillance and coast guard security ops. |
| 2013 | In 2013, Abdulla Yameen of the opposition PPM was elected to power. The Presidential Period of Yameen saw major strains in the India-Maldives ties. India raised objections to Yameen’s imposition of emergency. Yameen adopted pro-China policies. Yameen signed FTA with China & invited Chinese companies in for a number of major investments including the Hullumale island housing projects and friendship bridge. On the other hand Yameen threatened to evict Indian pilots and personnel from Maldives. |
| 2018 | In 2018, Ibrahim Mohamed Solih won the presidential elections by defeating Yameen. He adopted India-First Policy. India was invited to start many infrastructure projects including the $500mn Greater Male connectivity project. In 2021, India-Maldives signed the Uthuru Thilafalhu project to maintain a coastguard harbour base for India. This sparked the India Out campaign. |
The election of Dr. Mohamed Muizzu who rallied support around the ‘India Out’ campaign will test the friendly India-Maldives relations. New Delhi is anxiously watching the developments in Maldives.
What is the Significance of Maldives for India?
Maldives holds enormous significance for India. The Significance of Maldives for India is mentioned below-
- Geo-Economic Significance- Maldives is strategically located at the crossroads of several important trade routes that run through the Indian Ocean. 50% of India’s external trade and 80% of India’s energy imports transit through the Sea lanes of communication (SLOCs) in the vicinity of the Maldives.
- Geo-Political Significance- Maldives has been a partner of India in many regional groupings. Maldives is a member of the Colombo Security Conclave (CSC), Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), SAARC, SASEC and SAGAR initiative of India. Maldives supports India’s permanent membership of UNSC.
- Security Significance- For India, Maldives is the first line of defence against terrorism, piracy on the high seas, drug trafficking, narcotics, and other maritime crime. Maldives geographical location makes it a ‘toll gate’ between the choke points of the western Indian Ocean (Gulf of Aden and the Strait of Hormuz) and the eastern Indian Ocean (Strait of Malacca).
- Indian Diaspora Significance- There is a sizeable Indian Diaspora in Maldives. Numerous Indians are employed in Maldives’ education, medical care systems, tourism and hospitality sector.
What have been the areas of Co-operation between India and Maldives?
India has been a major partner of Maldives in its development journey. The major areas of cooperation between India and Maldives are mentioned below-
Economic Cooperation
- The economic co-operation is a major pillar of cooperation between India and Maldives Relation. Mentioned below are some of the economic cooperation pillars-
- $500 million in grants and financing to support maritime connectivity.
- $800-million line of credit from the Export-Import Bank of India
- India emerged as Maldives’ 3rd largest trade partner in 2021.
- Maldives is an important tourist destination for many Indians. Tourism is the backbone of Maldives economy.
- The India-Maldives relationship suffered a setback when Maldives entered into a Free-Trade Agreement (FTA) with China in 2017.
- In August 2021, Afcons, an Indian company, signed a contract for the largest-ever infrastructure project in Maldives which is the Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP).
Infrastructure Cooperation: Development of sustainable infrastructure in Maldives is one of the main goals of India. India is developing many infrastructure projects in Maldives Like:-
- Greater Male Connectivity Project: India is developing one of the largest project infrastructure project in Maldives which aims to connect Male to Villingili, Gulhifalhu and Thilafushi islands through a series of bridges, causeways, and roads. The project is crucial for the proposed Gulhifalhu Port.
- It will be a major catalyst for the Maldivian economy in the future through jobs and economic activity.
- Uthuru Thila Falhu Project (UTF): India is undertaking the development of strategic harbour projects like Uthuru Thila Falhu Project (UTF). It will serve as a harbour for the coast guard of the Maldives National Defence Force
- Police Infrastructures: India has also undertaken the design and construction of 61 police infrastructures across the Maldives. This will contribute to improved access to policing and will ensure the safety and security of the communities in the islands.
- Hanimaadhoo International Airport Development project under an Indian credit line, will add a brand-new terminal to cater to 1.3 million passengers a year.
- National College for Policing and Law Enforcement (NCPLE):It was inaugurated by India’s External Affairs Minister in 2022. NCPLE is the largest grant project executed by India in Maldives.
Military and Security Cooperation
- Trilateral Maritime: Maldives relies heavily on trilateral maritime security cooperation with India and Sri Lanka. Hence, securing the maritime borders of the Maldives is one of the foremost priorities of Indian Government
- India and Maldives co-operate in maritime security, maritime domain awareness and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- India has donated Landing Assault Craft and 24 Utility Vehicles to Maldives in order to bolster maritime security.
- Action Plan for Defence: India has signed a comprehensive Action Plan for Defense in April 2016 to consolidate the India-Maldives defence partnership.
- Maldivian National Defence Force (MNDF): India provides the largest number of training opportunities for MNDF, meeting around 70% of their defence training requirements.
- Joint Exercises: India and Maldives conduct many security Joint Exercises like “Ekuverin”, “Dosti”, “Ekatha” and “Operation Shield”.
- Operation Cactus: India in 1988 to help the government of Maldives neutralize the coup attempt.
Humanitarian Assistance Cooperation
- India has always lent a helping hand to Maldives in humanitarian assistance. Mentioned below are some of the examples of humanitarian assistance
- India has signed an MoU with Maldives for High Impact Community Development Projects (HICDPs) in 2019. A number of socio-economic development projects are planned to be implemented in Maldives through these projects.
- India has provided 100,000 Covishield vaccines to Maldives in January 2021 during the peak of the pandemic. Through Operation Sanjeevani, India supplied 6.2 tonnes of essential medicines to Maldives in the fight against COVID 19. India has handed over two sea ambulances to the Ministry of Defence of Maldives.
- India provided assistance to Maldives during recovery efforts after the 2004 Tsunami. India also helped address the shortage of drinking water in Maldives in 2014 through Operation Neer.
Rehabilitation Centre:
- Signing of contract for the Addu reclamation and shore protection project.
- A drug detoxification and rehabilitation centre in Addu built with Indian assistance.
- The centre is one of 20 high impact community development projects being implemented by India in areas such as healthcare, education, fisheries, tourism, sports, and culture.
What are the Challenges in India-Maldives Relations?
India-Maldives relations suffer from a lot of challenges. Some of which are mentioned below:
Political Challenges
- ‘India Out‘ Campaign: The president-elect Dr. Mohamed Muizzu and the former president Abdulla Yameen have been vocal advocates in the ‘India Out‘ Campaign. Both leaders are opposed to India’s military presence in the Maldives. Since they will be wielding power in the Maldives, it will become a major challenge for India.
Radicalisation
- A large number of Maldive citizens had joined violent extremist organisations such as the Islamic State (IS). There has been a steady rise in recruits joining jihadi groups in Pakistan over the last decade. There is now a greater risk that terrorist organisations based in Pakistan will use Maldives as a staging ground for attacks on India and Indian assets.
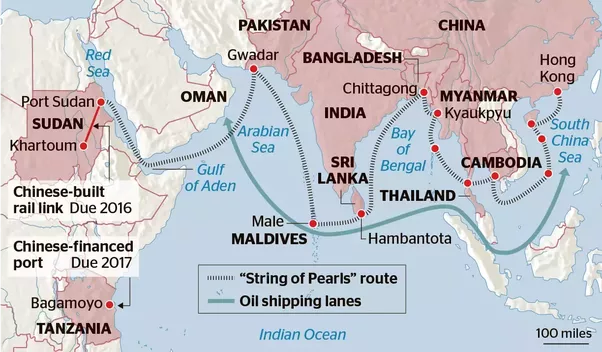
Growing Chinese Influence
- Maldives, like many other countries in the Indian Ocean region, has been a recipient of Chinese infrastructure investments.
- Maldives have massive Chinese investment and became a participant in China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). China funded and built various projects in Maldives, including the development of ports, airports, bridges, and other critical infrastructure as part of the “String of the Pearls” initiative.
- The pro-China stance led to a shift in Maldives’ traditional foreign policy, which had typically been closer to India. This shift created apprehensions in India about China’s growing influence in its immediate neighborhood and the potential strategic implications.
- The development of Chinese-controlled ports and military facilities in these areas has been seen as a challenge to India’s strategic interests and regional security.
- The India-Maldives relationship suffered a setback when Maldives entered into a Free-Trade Agreement (FTA) with China in 2017.
Climate Change
- As both India and Maldives are low-lying island nations, they are vulnerable to the effects of climate change, including rising sea levels and marine heatwaves. Maldives faces the risk of submergence.
What Should be the Way forward for India-Maldives Relations?
- Engage with the newly elected government- India must engage with the newly elected government of Maldives and address its concerns. India must convey that the projects being undertaken are for the general good of the people of Maldives. Ex- The redevelopment project at Hanimadhoo will improve tourist inflow as both the runway and terminal capacity will be increased. Tourism is the mainstay of Maldives econnomy.
- Increase the development assistance- India should increase development assistance to Maldives. India should target projects that have larger impact on general population of Maldives. This will enhance India’s goodwill among the people of Maldives. It will address concerns that have led to ‘India Out’ Campaigns.
- Timely Completion of Infrastructure Projects- Timely completion of infrastructure projects being undertaken by India like the Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP) will offer a credible and lucrative alternatives to Chinese projects.
- Target Youth Employment- India’s High Impact Community Development Projects (HICPs) in Maldives must include projects that aim to improve employability and foster entrepreneurship among the youth. This will help in countering the threats of radicalisation and extremism emanating from the soil.
- The newly elected regime of Maldives must understand that China’s entry in Maldives is solely to advance its own gains. A strong relationship with India will be to Maldives’s benefit.
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Different Operations in Maldives
- Operation Cactus 1988: Under Operation Cactus the Indian Armed Forces have helped the government of Maldives in the neutralization of the coup attempt.
- Operation Neer 2014: Under Operation Neer India supplied drinking water to Maldives to deal with the drinking water crisis.
- Operation Sanjeevani: India supplied 6.2 tonnes of essential medicines to Maldives, under Operation Sanjeevani as assistance in the fight against COVID 19.
What is the ‘India out’ Campaign and ‘India First’ Policy?
| India Out Campaign | ‘India Out’ campaign- A political movement to mobilise people in Maldives against the presence of Indian military on Maldivian soil. The campaign got louder around key bilateral developments such as the signing of the Uthuru Thila Falhu (UTF) harbour development deal with India in February 2021 & India’s announcement of the opening of a consulate in the southern Addu Atoll. |
Supporters of the Campaign: Abdulla Yameen who was the President of Maldives from 2013 to 2018, joined the campaign. Yameen was Pro-China during his tenure. Yameen signed FTA with China and gave an ultimatum to India to withdraw two Indian helicopters from the strategically important Laamu and Addu atolls. The current president designate Dr. Mohamed Muizzu rallied support around the ‘India Out’ campaign.  | |
| India First Policy | India First Policy- Maldives preference for India as the first choice in security partnership, socio-development assistance, and COVID response (Vaccines). |
| Proponent of the Policy: Ibrahim Mohamed Solih after he became the president in 2018 adopted the India First Policy. This Policy aimed to reverse the anti-India policies of Yameen between 2013-2018. |
